Biotin anti-human CD158e1 (KIR3DL1, NKB1);Clone#:DX9Host/Isotype:Mouse IgG1, κ
详细描述
|
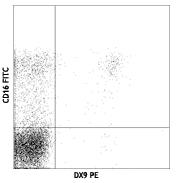 Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with DX9 PE and CD16 FITC |
| Description: |
CD158e1, also known as NKB1, is a 70 kD member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed on a subset of natural killer cells and T cells at varying levels among individuals. NKB1 is a type I membrane protein containing two immunoglobulin C2-type domains. The interaction of NKB1 with specific HLA-B antigens on a target cell (the HLA-Bw4 allele, for example) inhibits cytotoxicity and prevents target cell lysis and death. The interactions between KIR and MHC class I are thought to be important in NK and T cell regulation following antigen stimulation. The absence of ligands for KIRs may lower the threshold for activation through activating receptors and increase inflammation and susceptibility to autoimmune disease. |
| Other Names: |
NKAT3, NKB1, KIR-NKB1, p70 |
| Structure: | Immunoglobulin superfamily member, contains two immunoglobulin C2-type domains, 70 kD type I membrane protein |
| Distribution: | Subset of NK and T cells |
| Function: | Inhibits cytotoxic function of NK and T cells upon interacting with specific HLA-B antigens on target cell |
| Ligand Receptor: | HLA-B antigens such as the HLA-Bw4 allele |
| Antigen References: |
1. Colonna M, et al. 1995. Science 268:405. |

